Obstructive Pulmonary Disease-
-Asthma-
-The classic signs of symptoms of asthma are intermittent dyspnea, cough and wheezing. It can be considered a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
-Reactive airway disease is a term that describes some to the features of asthma
-Some common triggers of asthma include: allergens, exercise and viral infections
-Symptoms of asthma are episodic
-Patients usually have a history or family history of atopy (atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, and conjunctivitis)
-Physical exam may real nasal polyps or pale swollen nasal cavities with allergic rhinitis
-May have episodic wheezing and coughing
-Spirometry reveals a obstructive pattern which shows a reduction of the FEV1 to FVC
-If the FEV1/FVC is less than 0.70 airflow obstruction is present
-A key characteristic of asthma is reversibility. Acute reversibility is assessed after administration of short acting bronchodilator after 10-15 minutes. An increase of the FEV1 by 12 percent or more, with an absolute increase of at least 200 mL in the FEV1, indicates reversibility.
-Bronchoprovocation testing is useful for those who have normal spirometry prior to testing. Administration of a methacholine is used to stimulate bronchoconstriction
-Peak expiratory flow is a test that can be done in a doctors office. A reduced PEF that increases by 20 percent 10-20 percent after administration of quick acting bronchodilator implies the presence of asthma
-Chest X Ray is indicated with the following: fever, chronic purulent sputum production, persistent localized wheezing, hemoptysis, weight loss, clubbing, inspiratory crackles, significant hypoxemia, and moderate or severe airflow obstruction that does not reverse with bronchodilators
-Wheezing can also be caused by luminal narrowing in the respiratory tract including glottis, trachea, and bronchi, as well as vocal cord dysfunction.
-Cough can also be caused by rhinitis, sinusitis, GERD, post viral tussive syndrome, and eosinophilic bronchitis, Bordetella pertussis, and cough induced by ACE inhibitors
-Dyspnea can also be caused by COPD, heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary embolism, and sarcoidosis
-Asthma has 3 classifications based on:
1. Reported daytime and night time symptoms and exercise limitations over the previous 2-4 weeks
2. Current values of peak expiratory flow or FEV1/FVC
3. Number of exacerbations requiring oral glucocorticoids in the last year
-Intermittent asthma is characterized by symptoms occurring 2 or fewer times a week, two or few nocturnal a wakings, beta 2 agonist to relieve symptoms less than 2 a week, no interference with normal activities, PEF and FEV1 measurements when asymptomatic are normal, or one or less exacerbations requiring oral glucocorticoids in the last year.
-Mild asthma is characterized by normal FEV1 and peak flow measurements and the presence of the following: symptoms more than 2 days a week, 3-4 nocturnal a wakings per month due to asthma, use of beta 2 agonists more than 2 times per week, minor interference with normal activities, and two or more exacerbations requiring oral glucocorticoids per year
-Moderate asthma is characterized by the following: daily symptoms of asthma, nocturnal awakenings more than once a week, daily need for short term beta two agonists for symptom relief, more than minor limitation in normal activity, and a FEV1 between 60-80 percent of predicted
-Severe asthma is those patients that require high lose inhaled steroids or near continuous oral glucocorticoid treatment to maintain control of their asthma
-A cornerstone to asthma therapy is trigger avoidance
-Short term beta agonists have a rapid onset within 5 minutes and have a duration of 4-6 hours. Patients should take their short term beta agonists 10-20 minutes prior to exposure of trigger such as exercise
-Ipatroprium is less effective than beta agonists in the treatment of asthma. It is an anti-cholinergic
-Cromolyn Sodium aerosol helps prevent mast cell degranulation. Not to used in an acute attack. Should be used as a maintenance medication if necessary. Not as widely used as once was.
-Inhaled glucocorticoids reduces the frequency of symptoms and the need for inhaled bronchodilators. They are indicated for all patients with asthma
-Long acting beta agonists have a duration of action of at least 12 hours. Should only be given in combination therapy in combination with an inhaled steroids
-Leukotriene inhibitors (Singulair and Accolate) inhibit potent chemical mediators in asthma. These are preventive agents only. Not to be used in an acute attack
-Theophylline is an alternative sustained released bronchodilator was used as a controller for persistent asthma. It is no longer preferred because of side effects and blood levels must be monitored to avoid toxicity
-Bronchiectasis-
-Bronchiectasis has inflamed and easily collapsible airways, and obstruction to airflow. The diagnosis is made clinically by the basis of chronic daily cough with viscid sputum production, and the presence of bronchial wall thickening and luminal dilation on CT scan of the chest
-Induction of bronchiectasis includes an infectious insult, impaired drainage, airway obstruction, or a defect in host defense
-Numerous etiologies that cad induce or contribute to the pathophysiologic process that result in bronchiectasis: foreign body aspiration, defective defense hosts, cystic fibrosis, Young's Syndrome, rheumatic disease, dyskinetic cilia, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, and cigarette smoking
-PFT's may demonstrate an obstructive pattern
-Deciding if a patient has an acute exacerbation upon systemic changes rather than any specific lab feature.
-Acute bacterial infections are usually manifested by increased production of sputum that is more viscous and darker in color
-Fever and chills is generally absent in acute attacks
-Chest X-Ray should be performed with patients with respiratory distress
-Frequently common organisms colonized with bronchiectasis include: H. Influenzae, M. Catarrhalis, S. Aureus, and Pseudomonas
-Most afebrile stable patients can be treated as an outpatient
-Indications for inpatient treatment include: respiratory rate greater than 25 breaths per minute, Temp over 38 degrees C, hypoxemia, or failure to improve after oral antibiotics
-Two organisms difficult to eradicate with bronchiectasis include mycobacterium avium complex and aspergillus species
-Macrolides can be used for those who have recurrent infections
-Bronchodilators and steroids should be used for symptomatic control
-Yearly influenza vaccine is recommended for patients with bronchiectasis
-Pulmonary rehabilitation has been shown to be benefit of patients with bronchiectasis
-Resection of the disease portion of the lung can be used in severe instances when appropriate
-Chronic Bronchitis-
-Chronic bronchitis is defined as a chronic productive cough for 3 months in each of two successive years for whom all other causes of chronic cough have been rule out
-Chronic bronchitis is often due to smoking
-Patients can also get chronic bronchitis from breathing toxic gas or fumes.
-Symptoms of chronic bronchitis include fatigue, productive cough, shortness of breath, and chest tightness
-Should have an X-Ray to exclude other causes of chronic cough such as pneumonia, lung cancer, or bronchiectasis
-Chronic bronchitis is managed with bronchodilators and steroids for symptomatic relief. Oxygen may be needed for those with chronic hypoxemia. Pulmonary rehabilitation has been shown to be helpful
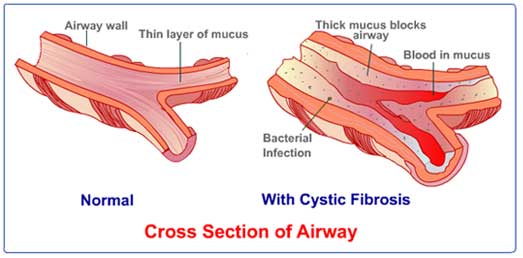
-Cystic Fibrosis-
-Cystic fibrosis is an exocrine and endocrine disorder. CF is caused by mutations in the transmembrane conductance regulator gene.
-Pulmonary disease is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with CF
-Ivacaftor is a small molecular weight oral drug used to treat patients who have a mutation in at least one of the CF transmembrane conductance regulator genes
-The course of CF is characterized by chronic infection with multiple organisms causing a gradual decline in pulmonary function, with period acute exacerbations that show increase sputum production, and shortness of breath
-Azithromycin is recommended for empiric treatment for those patients with CF
-Chronic treatment with nebulizer antibiotics to target pseudomonas with tobramycin appears to improve lung function
-There is limited evidence to guide decisions about use of beta 2 agonists. There is limit evidence to suggest they decree the frequency of exacerbations or the quality of life. Only beneficial as rescue medications
-Anticholinergic agents such as ipatroprium can induced bronchodilation following administration in patients with CF
-The endonuclease DNase can decrease the viscosity of purulent CF sputum by cleaving strands of denatured DNA that are released by neutrophils
-Hypertonic saline has been shown to be beneficial in patients over 14 years of age. It has been shown to hydrate inspissated mucus that is present in the airways of patients with CF
-Mucomyst has not been shown to be beneficial in CF
-Chest Physiotherapy remains a pillar of those CF patients that continuously produce sputum
-Macrolide therapy is found to be beneficial for those with CF who have bronchitis
-High dose ibuprofen has been shown to be of value in patients with mild CF disease because of anti-inflammatory properties
-Influenza vaccine, the pneumococcal vaccine and synagis vaccine is recommended for patients with CF
-BiPAP has been used to be beneficial in patients with CF the have retained CO2 levels
-Lung transplantation in CF usually requires transplanting both lungs
-Gastrointestinal manifestations of CF can be broken down into intestinal, pancreatic, and hepatobiliary manifestation
-Intestinal pathology includes: GERD, meconium ileus, distal intestinal obstruction, intussusception, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, constipation, and rectal prolapse
-Pancreatic insufficiency is present from birth in patients with CF. Insufficient secretion of enzymes leads to malabsorption of fat (with steatorrhea) and protein. The fat malabsorption can lead to deficiencies of fat soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. Patients with CF are prone to chronic pancreatitis
-Hepatobiliary manifestations include asymptomatic liver disease. Usually found at autopsy. Antemortum elevations of alkaline phosphatase is usually found in about 10 percent of the patients with CF
-The mainstay of treatment of pancreatic insufficiency is pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy
-Emphysema-
- COPD has subtypes which include chronic bronchitis, chronic obstructive asthma, and emphysema
-Emphysema is abnormal and permanent enlargement of the airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles that is accompanied by destruction of the airspaces walls, without fibrosis
-Exclusion of fibrosis is necessary to distinguish alveolar destruction due to emphysema from that due to interstitial pneumonia
-It is common for emphysema patients to have moderate to severe airway obstruction
-Many subtypes of emphysema including: proximal acinar, panacinar, and distal acinar
-Emphysema can have variable ways of presenting. Patients may present with a sedentary lifestyle and avoid exertional activity. Patients present with respiratory symptoms and chronic cough, and patients present with increased cough, wheezing and purulent sputum
-Physical exam reveals prolonged expiatory phase, hyperinflation, and increased resonance to percussion. May have decreased breath sounds, wheezing, or crackles in the lung bases. Heart sounds maybe distant. Patients may tripod or have pursed lipped breathing. Clubbing is uncommon with COPD patients
-Spirometry shows a decreased FEV1/FVC that sides not improve with bronchodilator therapy (if does not have asthma component)
-Lung volumes and capacities are increased with COPD
-ABG's may demonstrate low Pa02, chronic PaCO2 retention, and metabolic compensation with increased HCO3
-Treatment is symptomatic similar to asthma. Beta 2 agonists for acute rescue relief. Anticholinergics such as ipatroprium are effective. Combination long term beta agonists with combination inhaled steroids can be used. Glucocorticoids are given during exacerbations
-Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AAT)- is associated with pulmonary emphysema and several forms of liver disease, cirrhosis, neonatal hepatitis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
-The discovery of AAT protein has allowed for replacement therapy. IV augmentation of AAT protein is currently most direct efficiency of elevating AAT levels in the plasma and lungs



I was diagnosed of Herpes 2years ago and I have tried all possible means to get the cure but all to no avail, until i saw a post in a health forum about a Herbal Doctor(Dr imoloa who prepares herbal medicine to cure all kind of diseases including Herpes, at first i doubted, if it was real but decided to give him a trial, when i contacted Dr imoloa through his Email: drimolaherbalmademedicine@gmail.com he guided me and prepared a herbal medicine and sent it to me via courier Delivery service,when i received the package (herbal medicine) He gave me instructions on how to consume it, i started using it as instructed and i stop getting outbreaks and the sores started vanishing, could you believe i was cured of this deadly virus within two to three weeks and notices changes in my body. Days of using this REMEDY,couldn't believe the healing at first until i see it as my HERPES get cleared like magic Dr imoloa also use his herbal medicine to cure diseases like, HIV/aids, lupus disease, dry cough, fever, malaria, bronchitis disease, Lyme disease, acute myeloid leukaemia, alzheimer's disease, blood poisoning, measles, kidney cancer, kidney infections, diarrhoea, epilepsy, joint pain, mouth ulcer,bowel cancer, discoid eczema, eye cancer, food poisoning, fibroid, hairy cell leukaemia, mouth cancer, skin disease, lung cancer, liver disease, penile cancer, parkinson disease, arthritis, breast cancer, bone cancer hepatitis A.B.C, Diabetes, fatigue, muscle aches, anal cancer, asthma, Contact this great herbal Doctor today the father of herbalism. via Email: drimolaherbalmademedicine@gmail.com or whatssapp him +2347081986098. and get cured permanently He is real..
ReplyDelete